Artificial intelligence (AI) is hot right now. Also hot: the data centers that power that technology, which require a tremendous amount of energy.
In 2022, data centers used more than 4% of all electricity in the U.S., with 40% of that energy spent to keep equipment cool. As demand on data centers increases, even more energy will be required.
To mitigate that, the U.S. Department of Energy has awarded more than $40 million to researchers to find new ways to cool data centers. University of Missouri researcher Chanwoo Park recently received nearly $1.65 million from that initiative, known as COOLERCHIPS.
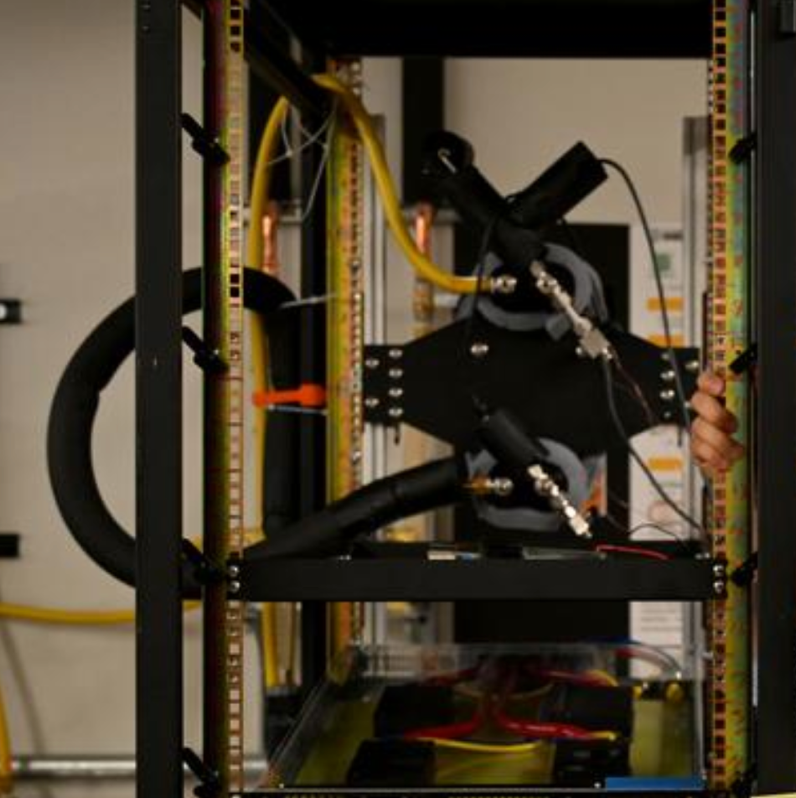
Two-phase cooling system designed to efficiently dissipate heat
Currently, data centers are cooled with either air-moving fans or liquid that moves heat away from computer racks. But Park and his team are developing a new two-phase cooling system designed to efficiently dissipate heat from server chips through phase change, such as boiling a liquid into vapor in a thin, porous layer. The new system can operate passively without consuming any energy when less cooling is needed.
“Even in active mode, where a pump is used, it consumes only a negligible amount of energy. The liquid goes in different directions and evaporates on a thin metal surface,” Park said in a statement. “Using this boiling surface, we’re able to achieve very efficient heat transfer with low thermal resistance.”
“Drastically reduce” cooling energy needed
The system also includes a mechanical pump that is activated to absorb more heat only when needed. Early tests show that two-phase cooling techniques “drastically reduce” the amount of energy needed to keep equipment cool.
“Eventually, there will be limitations under current cooling systems, and that’s a problem,” Park said. “We’re trying to get ahead of the curve and have something ready and available for the future of AI computing.”
Citation: R. Kokate and C. Park (2024). Experimental analysis of subcooled flow boiling in a microchannel evaporator of a pumped two-phase loop. Applied Thermal Engineering, 249, 123154. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1359431124008226?via%3Dihub (open-access)
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)