In another step toward nanofluidic-based neuromorphic (brain-inspired) computing, EPFL (École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne) engineers have executed a logic operation by connecting chips that use ions rather than electrons to process data, avoiding the rising energy cost of computers.
On Friday, March 14, Mindplex News presented two approaches to creating synapse-like more efficient analog memristors (memory resistors): a paper-based photoelectronic device and a circuit crossbar array.
Nanofluidic memristive device
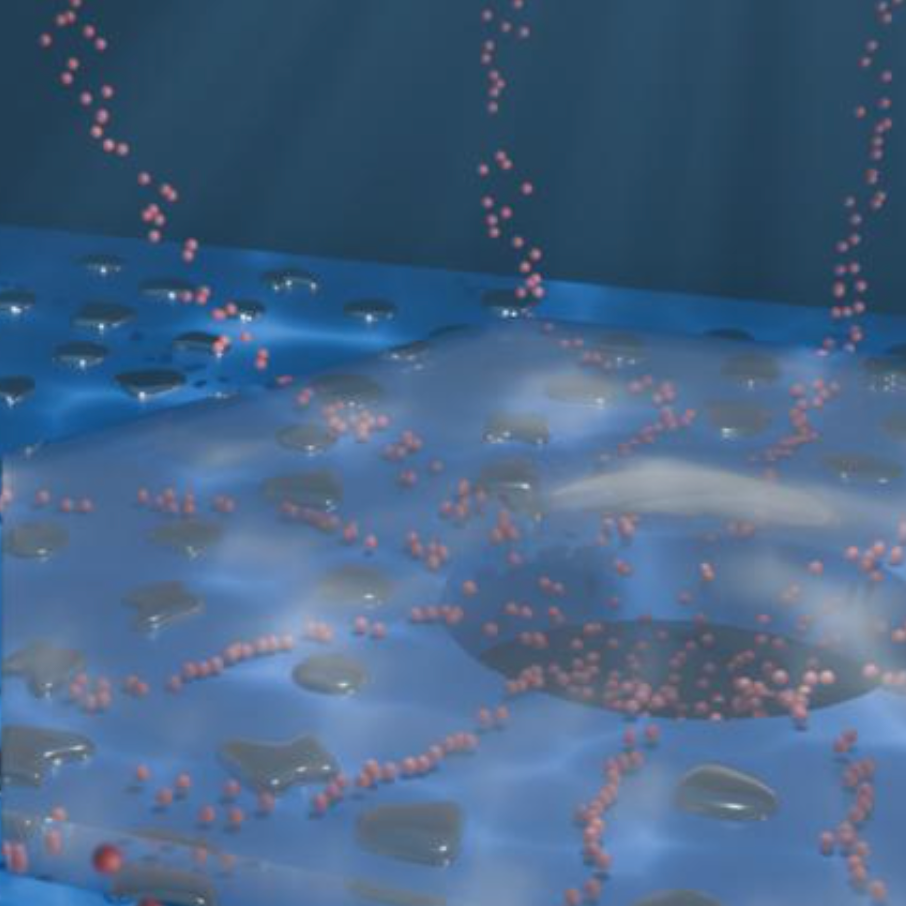
As published in Nature Electronics today (March 19, 2024), researchers at the EPFL Laboratory of Nanoscale Biology have explored a third approach: a nanofluidic memristive device that relies on ions in a nanofluidic neural network, closely mimicking the brain.
“We have fabricated a new nanofluidic device for memory applications that is significantly more scalable and much more performant than previous attempts,” says LBEN postdoctoral researcher Théo Emmerich. “This has enabled us, for the very first time, to connect two such ‘artificial synapses,’ paving the way for the design of brain-inspired liquid hardware.”
Just add water
For their study, the researchers immersed their device in an electrolyte water solution containing potassium ions, but others could be used, including sodium and calcium.
“We can tune the memory of our device by changing the ions we use, which affects how it switches from on to off, or how much memory it stores,” Emmerich explains.
The device was fabricated on a chip at EPFL’s Center of MicroNanoTechnology by creating a nanopore* at the center of a silicon nitride membrane, inside a synapse.*
Liquid Circuits
Their next goal is to connect a network of highly asymmetric channels (HACs) with water channels to create fully liquid circuits. In addition to providing an in-built cooling mechanism, the use of water would facilitate the development of biocompatible devices, with potential applications in brain-computer interfaces or neuromedicine.
* The researchers added palladium and graphite layers to create nano-channels for ions. As a current flows through the chip, the ions percolate through the channels and converge at the pore, where their pressure creates a blister between the chip surface and the graphite. As the graphite layer is forced up by the blister, the device becomes more conductive, switching its memory state to ‘on’. Since the graphite layer stays lifted, even without a current, the device ‘remembers’ its previous state. A negative voltage puts the layers back into contact, resetting the memory to the ‘off’ state.
Citation: Emmerich, T., Teng, Y., Ronceray, N. et al. Nanofluidic logic with mechano–ionic memristive switches. Nat Electron (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01137-9 (open-access)
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)