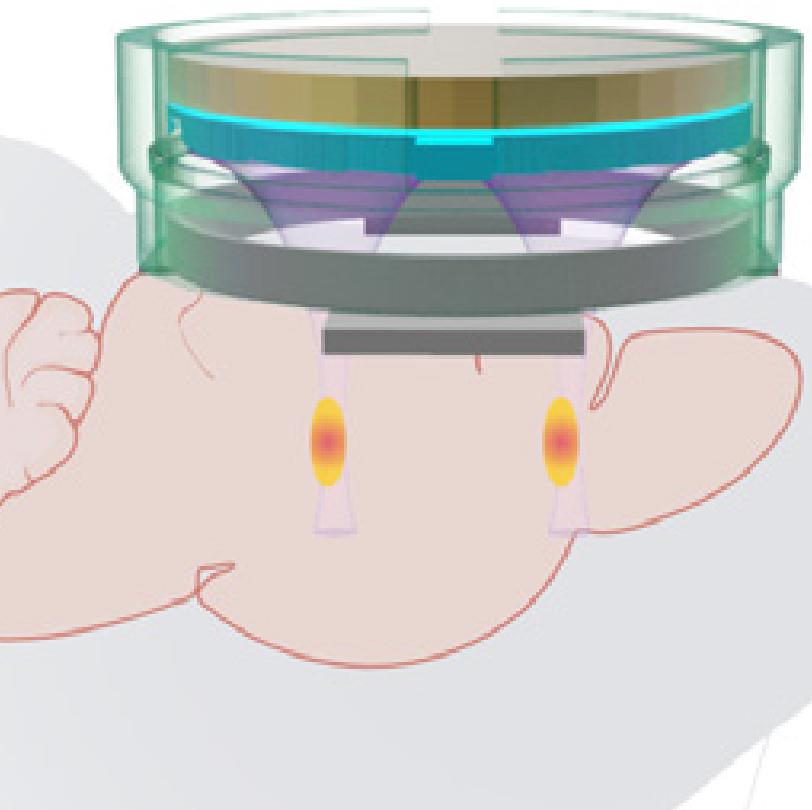
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed a noninvasive technology to treat human brain diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, that simultaneously involve damage in various regions of the brain. The holographic acoustic device, combined with genetic engineering, precisely targets affected neurons in selected cell types at multiple diseased brain regions.
Hong Chen, associate professor of biomedical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering and of neurosurgery in the School of Medicine, and her team created the noninvasive “AhSonogenetic” device to alter genetically selected neurons in the brains of mice. The results of the study were published June 17 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Multiple technologies
AhSonogenetics combines several of Chen’s group’s recent advances. In 2021, she and her team launched Sonogenetics, a method that uses focused ultrasound to deliver a viral construct containing ultrasound-sensitive ion channels to genetically selected neurons in the brain. They use non-invasive low-intensity focused ultrasound to deliver a small burst of warmth, which opens ion channels and activates the neurons. Chen’s team was the first to show that sonogenetics could modulate the behavior of freely moving mice.
In 2022, the team designed and 3D-printed a flexible and versatile tool known as an Airy beam-enabled binary acoustic metasurface, which allowed them to manipulate ultrasound beams. She is currently developing Sonogenetics 2.0, which combines the advantage of ultrasound and genetic engineering to modulate defined neurons noninvasively and precisely in the brains of humans and animals. AhSonogenetics brings them together as a potential method to intervene in neurodegenerative diseases.
Sonogenetics gives researchers a way to precisely control brains, while airy-beam technology allows researchers to bend or steer the sound waves to generate arbitrary beam patterns inside the brain at high spatial resolution.
Treating Parkinson’s disease
Chen’s team tested the technique on a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. With AhSonogenetics, they were able to stimulate two brain regions simultaneously in a single mouse, eliminating the need for multiple implants or interventions. This stimulation alleviated Parkinson’s-related motor deficits in the mouse model, including slow movements, difficulty walking and freezing behaviors.
The device, which costs roughly $50 to make, can be tailored in size to fit various brain sizes, expanding its potential applications. The design file for the Airy-beam holographic transducer is available on GitHub: https://github.com/ChenUltrasoundLabWUSTL/AiryBeam_Lens_Design. Funding was provided by the National Institutes of Health.
Citation: CitHu Z, Yang Y, Gong Y, Chukwu C, Ye D, Yue Y, Yuan J, Kravitz AV, Chen H. Airy-beam holographic sonogenetics for advancing neuromodulation precision and flexibility. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences June 17, 2024. DOI. 10.1073/pnas.2402200121 (open access)
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)