Tiny robots controlled by magnetic fields for targeted drug delivery
Oct. 25, 2024.
2 mins. read.
10 Interactions
These tiny robots, around the size of a rice grain, are controlled by magnetic fields and are safe to use inside the body.
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University (NTU) have developed grain-sized robots that could have significant medical and industrial uses.
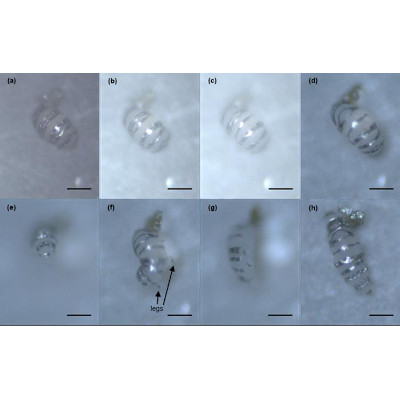
These tiny soft robots, around the size of a rice grain, are made from biocompatible materials that are safe to use inside the body. The scientists describe the methods and results of this study in a paper published in Advanced Materials.
Each robot is embedded with magnetic particles, allowing it to be controlled by magnetic fields. Using an external electromagnetic coil system and a computer, researchers can manipulate the robots’ movements with high precision in six different directions: forward, backward, left, right, up, and down, along with rotational motion on each axis. This flexibility, known as “six degrees of freedom,” enables the robots to perform delicate tasks and reach areas that larger instruments cannot access.
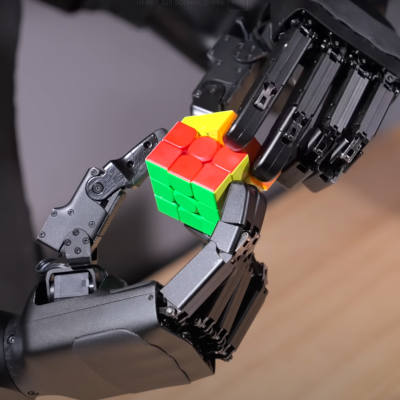
The NTU team created various prototypes to demonstrate potential uses. One version of the robot, inspired by jellyfish, swims through water and can squeeze through tight spaces. This ability could allow it to reach delicate areas in the human body, like the brain, for minimally invasive procedures.
Another prototype functions as a “gripper,” able to pick up and assemble tiny structures, making it promising for building small-scale devices in “micro-factories” where intricate assembly is required. In lab experiments, these robots performed tasks faster and with more precision than previous models.
Applications and future developments
The researchers emphasize that the key to their success was a deep understanding of the physics of magnetic fields, allowing them to optimize the robots’ movement and control.
The development has broad applications, especially in the field of targeted drug delivery, where such tiny robots could deliver medicine directly to hard-to-reach parts of the body. Beyond medicine, the technology might also be used in manufacturing for the assembly of micro-scale products. Though this research shows promise, the team plans further tests to ensure these robots are ready for practical use, especially in clinical settings. Future developments may include making the robots even smaller, potentially on the scale of a few hundred micrometers, and increasing their autonomy, which means they could operate without constant external control.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)






2 Comments
2 thoughts on “Tiny robots controlled by magnetic fields for targeted drug delivery”
What are the specific biocompatible materials used in the construction of these soft robots, and how do they ensure safety within the human body?
🟨 😴 😡 ❌ 🤮 💩
Polymers laced with magnetic particles.
🟨 😴 😡 ❌ 🤮 💩