AI and Creativity: Exploring the Realms of Machine-Generated Artistry
Apr. 23, 2024.
13 min. read.
26 Interactions
Eric delves into the evolving landscape where AI intersects with creativity, questioning the authenticity and autonomy of machine-generated artistry. Can AI truly innovate, or does it merely echo human input?
The concept of creativity has long been thought to be the exclusive domain of human intellect, a defining feature that sets us apart from machines. However, the rise of artificial intelligence has compelled us to reconsider what constitutes creativity and whether it can manifest within the realms of silicon and software. But can machines exhibit true creativity, or is their apparent ingenuity merely a reflection of our own ideas and instructions?
We live in an era where machines produce art, generate new musical compositions, and even write poetry (if you truly believe that to be a poem), leading to intense debate within philosophy, computer science, and the arts. The Artist in the Machine explores this intersection between AI-powered creativity and human artistic expression, while others seek to understand the creative process through AI.
The journey into AI’s role in creative domains touches upon intriguing philosophical discussions and practical implications, ranging from the future of work to the very nature of art itself. We evaluate whether the creative outputs of AI challenge our understanding of human creativity or if they follow elaborate patterns pre-designed by their creators. It is an exploration of whether AI-driven creativity is a reality or a carefully crafted illusion, a question we continue to ponder as technology evolves.
Defining Creativity in AI
In our understanding of artificial intelligence, we recognize creativity as a pivotal topic of discussion. Here, we dissect the nuances behind AI creativity, setting a firm foundation for exploring its potential and limitations.
AI Mimicry vs. True Creativity
AI Mimicry involves replicating existing styles or ideas. It’s a technical feat where AI learns from huge datasets to produce something recognizable and familiar. For instance, an AI might generate a painting in the style of Van Gogh, but is it truly creative? True Creativity, on the other hand, requires originality and the capacity to generate novel and valuable work. Can AI cross this threshold from mimicry to genuine innovation? Not anytime soon.
Philosophical Foundations
The question of whether AI can be creative touches deep philosophical foundations. Creativity is often seen as an inherently human attribute linked to consciousness and intent. Examining whether AI, void of self-awareness, could possess the qualia or the subjective experience of creativity, which some philosophers argue is vital for true creativity.
Technological Parameters
Within the realm of Technological Parameters, the focus is on the algorithms and computational processes that enable AI to perform tasks associated with creativity. This includes understanding machine learning techniques that allow AI to ‘learn’ from data and potentially develop new patterns or solutions. Can the parameters we set and the algorithms we develop foster an environment in which AI demonstrates creativity? This is a question that is being actively investigated, with the knowledge that the answer has significant implications for the future of AI and creativity.
Historical Evolution of AI in Art and Creativity
Artificial Intelligence has transformed art and creativity, continually blurring the lines between technology and human ingenuity. We’ll explore the roots and progression of AI in the realm of creative expression.
Early Computational Creativity
AI’s role in art can be recognized as the initial phase of Early Computational Creativity. This encapsulates the foundational work in AI involving simple algorithms capable of generating novel patterns and structures. One of the first instances of computer-generated art dates back to the 1950s when Ben Laposky used an oscilloscope to produce his “Oscillon” electronic pictures.
By the 1970s, Harold Cohen’s AARON program became one of the most significant early systems, as it demonstrated that computers could not only generate random patterns but also create complex, rule-based artistic compositions. This period set the groundwork for future exploration in the field, indicating that machines had the potential to partake in the creative process.
Pioneering Projects and Systems
There were Pioneering Projects and Systems that have shaped the current landscape of computational creativity. Significantly, the advent of algorithmic art and the development of software like Adobe Photoshop facilitated artists in creating digital art.
The introduction of machine learning models, particularly generative adversarial networks (GANs), gave rise to a new wave of creativity. These systems could now learn from vast datasets of artworks, leading to the creation of art that, in some cases, is indistinguishable from that of human artists. Here, we observe projects such as The Next Rembrandt, which used deep learning to generate a new artwork in the style of the Dutch master, pushing the frontier of what’s considered “creative” in the context of machine capability.
AI Tools and Methods for Creative Endeavors
In the realm of creative AI, we have developed and refined various tools and methods. Each serves a unique purpose in fostering machine-driven creativity, ranging from pattern recognition to generating novel content.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are the backbone of AI creativity. These algorithms learn from large datasets, identifying patterns and making predictions. Applications include data-driven design, content generation, and assisting in creative decision-making. For instance, a machine learning model might analyze music from different genres to help create a new piece that fuses these styles seamlessly.
Generative Adversarial Networks
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) involve two competing neural network models: one generates candidates (the generator), and the other evaluates them (the discriminator). The push and pull between these networks leads to the generation of highly refined and sophisticated outputs. In the visual arts, GANs have been used to craft artworks that are indistinguishable from those made by human hands.
Evolutionary Computing
Evolutionary Computing draws inspiration from natural selection. Here, we design algorithms that simulate evolution, allowing solutions to problems to arise organically over time. Solutions mutate and combine, with the best ones surviving to inspire the next generation. This method has helped create innovative architectural forms and optimized design layouts without human bias.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Neural Networks and Deep Learning are at the forefront of advancing AI creativity. By simulating the workings of the human brain, these networks can recognize complex patterns and make connections that are not immediately obvious. Such techniques are instrumental in developing AI capable of natural language generation and improvisational interactive performances.
Each method enriches our arsenal of AI tools, enabling machines to contribute uniquely to creative endeavours. Through our continued research and development, we fortify the bridge between artificial intelligence and human creativity.
Evaluating AI-Generated Art and Creativity
We find ourselves probing the boundaries of creativity at the intersection of art and technology. As AI continues to produce complex works, we are tasked with developing robust methods to evaluate these new forms of expression.
Criteria for Creativity
Originality and Novelty: The hallmark of creativity, whether human or artificial, hinges on producing original and novel work. For AI-generated art, this means the algorithms should create pieces that are not mere reiterations of its training data but offer something unforeseen.
Complexity and Skill: We assess the complexity of the artwork and the proficiency with which the AI applies artistic techniques. Does the AI exhibit mastery over various styles, forms, and textures?
Role of Human Perception
Perceptual Engagement: It’s essential to consider how AI-generated art impacts human emotions and cognitive engagement. Does the art evoke a strong aesthetic response or elicit contemplation?
Authenticity Perception: There is an inherent bias in how we perceive art created by machines versus humans. Our challenge lies in overcoming these perceptions to evaluate art based on its intrinsic qualities rather than its origins.
Comparing with Human-Made Art
Innovation versus Imitation: A crucial comparative aspect is whether AI art pushes boundaries like human artists do or if it primarily mimics existing styles. Are AI creations contributing to the evolution of artistic genres?
Contextual and Conceptual Understanding: Human artists imbue their works with meaning and context. We must discern if AI-generated pieces possess layers of interpretation or remain confined to aesthetic patterns without deeper significance.
AI in Collaborative Art
This section explores the burgeoning intersection of artificial intelligence and human creativity. Our focus is on how AI contributes to collaborative art, enhancing the creative process through human-AI partnerships and interactive installations.
Human-AI Collaboration
We are witnessing a new era where artists and AI systems work hand in hand, creating works that are beyond the capabilities of either alone. This synergy of human intuition with machine’s computational prowess is exemplified in projects like “Design considerations for real-time collaboration with creative artificial intelligence,” where AI systems can contribute creatively in real-time, suggesting variations and alternatives that can inspire the human artist.
Interactive Art Installations
Art installations that incorporate AI are transforming spectators into active participants. Interactive art pieces facilitated by AI technology allow us to witness dynamic artworks that respond and evolve based on audience input.
One such example is detailed in the study, “It is your turn: Collaborative ideation with a co-creative robot through sketch,” demonstrating how these installations create a two-way communication channel between the audience and the artistic work.
Implications and Ethical Considerations
As we explore the realm of AI and creativity, we must consider the complex implications and ethical challenges that manifest. These concerns shape our approach to integrating AI into creative processes and industries.
Copyright and Ownership Issues
AI-generated content straddles a nuanced line of intellectual property law. The question arises: who owns the output produced by AI? Is it the creators of the AI or the users, or should the AI itself hold any rights? For instance, the book “The Artist in The Machine: The World of AI-Powered Creativity” may touch on these evolving legal frameworks as AI plays a more significant role in creative fields.
Authenticity and Attribution
The authenticity of AI-created works and the attribution of credit are complex issues. If an AI creates a piece of art, should it be recognized as the artist, or should all credit go to its human creators? Ethical practices necessitate transparent attributions, as highlighted by discussions in “The Ethics of Creative AI“. This ensures that consumers of AI-generated content know the origins and creators behind the work.
Societal and Cultural Impact
AI’s impact on society and culture can be profound. The integration of AI in creative endeavours could lead to job displacement and may change our perception of art and creativity. Our engagement must consider and mitigate potential negative impacts, a point inspired through research like “AI Creativity and the Human-AI Co-creation Model“. By doing so, we can harness AI’s potential while safeguarding our cultural heritage and societal norms.
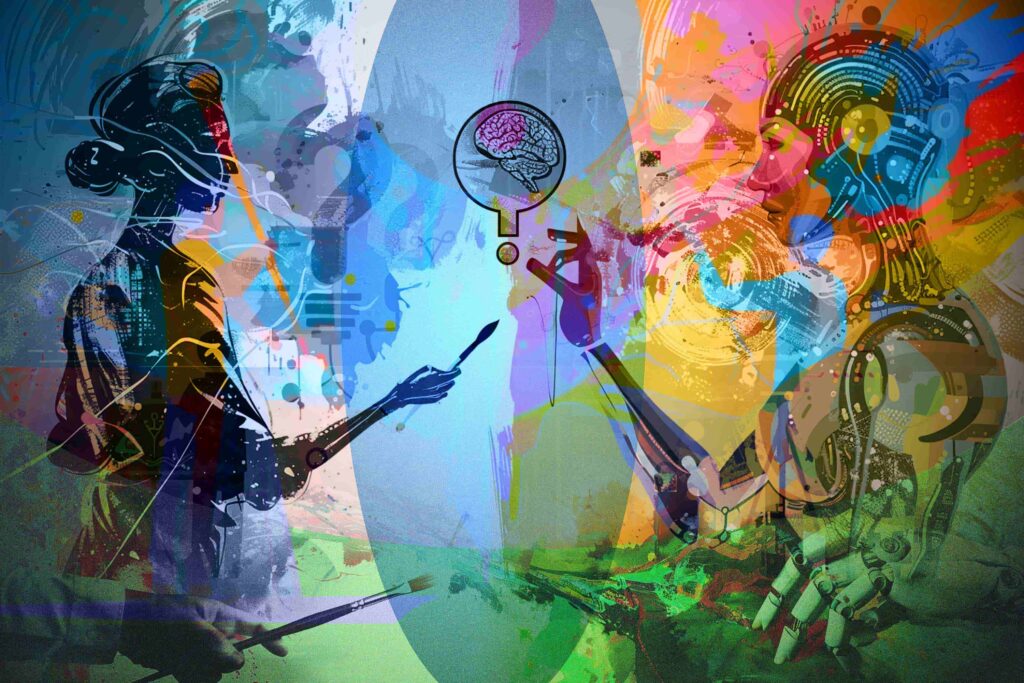

Future Directions for AI in Creativity
In exploring the future directions for AI in creativity, we must examine the ongoing advancements in computational creativity as well as the potential for AI systems to achieve autonomy in creative processes. Our focus lies on concrete progressions and implications in these fields.
Advancements in Computational Creativity
Recent developments have significantly enhanced the capabilities of AI in mimicking human-like creativity. Innovative algorithms now enable AI to compose music, generate novel artwork, and write poetry. For instance, the use of deep learning has permitted more sophisticated pattern recognition and emulation of artistic styles.
These advancements present numerous opportunities for collaborative creative efforts, where AI acts as an assistant to extend the reach of human creativity rather than replacing it.
Potential for Autonomous Creative AI
Looking ahead, the quest for truly autonomous creative AI raises crucial questions and possibilities. We see prototypes of AI that not only produce creative outputs but also evaluate and iterate on their work without human intervention.
The objective is to enable AI to understand the context and innovate, as highlighted by research exploring https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10400419.2022.2107850AI’s role in everyday creation processes. As AI tools become more independent, they could conceivably originate novel and valuable content, potentially leading to their recognition as standalone creators.
Case Studies
In exploring the potential for machines to exhibit creativity, we’ve analyzed various instances where artificial intelligence has been applied to the arts. Our findings provide concrete examples of AI-assisted creations across different artistic domains.
AI Composed Music
AI has been utilized in music to compose pieces that resonate with human emotions and styles. OpenAI’s Jukebox is an example of a neural network that generates new music in various genres after training on a vast song dataset. Notable outcomes include projects like AIVA, an AI that has been officially recognized by a music society for its original compositions, indicating moves toward AI not only imitating but also innovating in music composition.
AI Written Literature
Artificial intelligence has been making strides in literature by aiding in the creation of prose and poetry. The platform GPT-3, developed by OpenAI, has successfully written poems, short narratives, and even news articles that often require a second glance to distinguish from human-authored content. However, AI-written literature usually works best with human collaboration, exemplified by the interactive storytelling machine named Brutus that supports authors with ideation and drafting.
AI in Visual Arts
Visual arts have seen the emergence of AI that can paint, sketch, and even sculpt. DALL-E, another innovation from OpenAI, generates new visuals from textual descriptions, showcasing a capacity for originality and abstraction. Innovative tools like DeepDream and GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) have been used to create artworks that have been exhibited and sold, reflecting a growing appreciation of AI’s role in artistic expression.
Conclusion
In our examination of artificial intelligence and creativity, we’ve observed that the intersection of these fields is both promising and challenging. AI systems, like the storytelling capabilities of Brutus, show potential in areas traditionally reserved for human creativity. Yet, questions persist regarding the genuine creativity of machines.
We recognize that AI’s creativity often stems from human input and programming. However, the boundary between human and machine-generated creativity may blur as collaborations become more commonplace. We look at examples like AI in the art world, where machines complement human effort rather than replace it.
The debate over whether machines can be truly creative is ongoing. As tools for expression and innovation, AI systems can produce work that appears creative, but the depth of this creativity is under scrutiny. Our role is to guide and refine AI development, ensuring that it aligns with our evolving definition of creativity.
The future holds potential for AI to further integrate into creative processes, enhancing our capabilities and creating new artistic possibilities. Whether AI can be truly creative is a technological question and a philosophical one that we continue to explore.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)








1 Comments
One thought on “AI and Creativity: Exploring the Realms of Machine-Generated Artistry”
Good job mate. A compact and clear presentation of the history of machine creativity and artistic tooling. It was great to have this article under the topic of ethics.
The concept that got me thinking was the question about the agency behind a piece of artwork. I think it is actually a quite intuitive basis to start talking about a fuzzy, independent, dynamic agent behind an action in general. That is because to be able to go into more detailed discussion about things such as ownership or IP rights one has to identify the contributors.
I like to say that the agency actualizes locally for each decision. With AI there are probably many ways to quantitatively measure contributions of different participants. The impact chain behind the artistic output may be long and complex involving many different and different types of agents.
Artistic creativity has been one of the top application domains of new intelligent tech for a long time and perhaps it will play a crucial role also in its ethical evolution. Thanks for writing this article.
🟨 😴 😡 ❌ 🤮 💩