Layer-3 (L3) Networks: Climbing Crypto’s Next Frontier
Apr. 17, 2024. 7 mins. read.
11 Interactions
Unlocking Blockchain's features: Layer-3 networks explored. Discover how these advanced solutions enhance scalability, interoperability, and specialized functionality, shaping the next phase of crypto evolution.
Intermediate Level Introduction
Web3 and DeFi continue to grow and mature, and any established smart contract platform blockchain requires scaling and speed to keep up with user demands, causing a new frontier to emerge: Layer-3 chains.
These cutting-edge solutions are designed to build upon the foundation of Layer-1 and Layer-2 technologies, bringing forth a new era of scalability, interoperability, and specialized functionality.
Understanding the Blockchain Layers
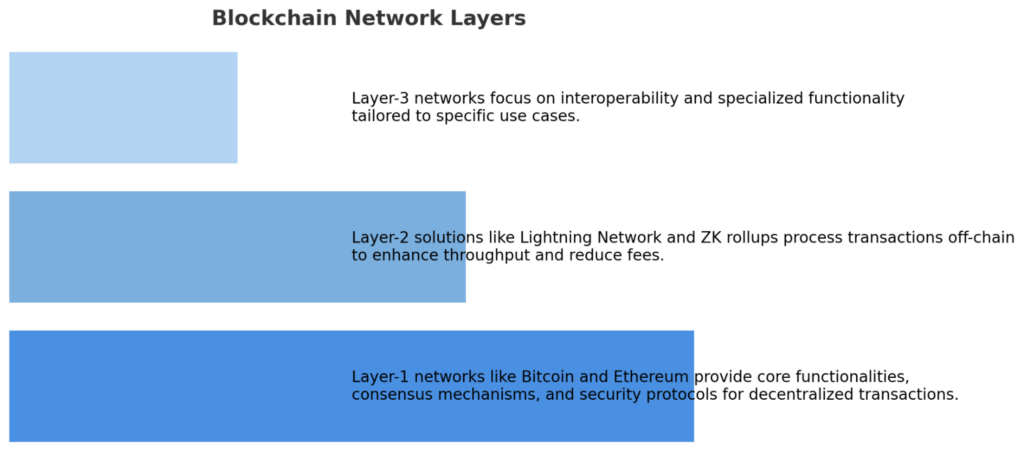
To understand why Layer-3 networks are being touted as integral to the future success of crypto, it’s essential to understand the role of each layer in the blockchain ecosystem.
Layer-1: The Foundation
Also called the base blockchain, Layer-1 networks, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana and Cardano form the bedrock of the blockchain world. They provide stability and battle-tested security to the projects that build on them, and rely on them to keep their assets safe.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two biggest L1 blockchains in the world. L1 blockchains are the basic infrastructure and security layer that Layer 2 (L2) blockchains build on. These networks provide the core functionalities, consensus mechanisms, and security protocols that decentralized transactions and applications require.
Layer-2: Scaling Solutions
Layer-1 networks face scalability challenges; Ethereum can process only 14 transactions per second maximum. So Layer-2 solutions have emerged in the last two years to address these limitations.
A Layer-2 chain is a secondary protocol that is built on top of an existing Layer-1 blockchain.
The primary purpose of Layer-2 chains is to improve the scalability and efficiency of the whole blockchain by handling transactions off the main ledger. This approach helps alleviate the network congestion. It also reduces the transaction costs – which are often high on Layer-1 blockchains due to their limited throughput.
Popular examples of Layer-2 solutions include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Optimism and Arbitrum for Ethereum. Layer-2 solutions employ various techniques like state channels, sidechains, rollups, and plasma, each with distinct mechanisms for moving transactions off the main blockchain.
As such, Layer-2 chains are critical in blockchain architecture, offering a balance between decentralized security and high scalability.
Optimistic vs ZK Proof Rollups
Rollups execute transactions outside the main chain, but post transaction data back to it. This setup enables higher transaction throughput while coming back to the robust security of the Layer-1 blockchain.
Ethereum rollups can broadly be divided into two camps, namely optimistic rollups (OR) and zero-knowledge proof (ZK) rollups.
Optimistic rollups like Optimism (Coinbase’s Base Network used its OP stack to build its chain) and Arbitrum assume transactions are valid by default, and only run computations in the event of a dispute, which significantly reduces the burden on the main blockchain but entails a waiting period of up to seven days for withdrawals to ensure security.
In contrast, ZK rollups like ZkSync and Stark use zero-knowledge proofs to validate all transactions off-chain before bundling them back to the main chain, providing immediate finality and reducing wait times but requiring more complex computation upfront. Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum creator, is a big fan of ZK rollups as they enable you to validate data without the need to share your private information.
Layer-3: The use case-specific layer
However, if the world wants to all transact and send data on one chain like Ethereum or Solana, we need to go bigger and faster. This is where Layer-3 chains come in.
Layer-3 networks focus on enabling seamless interoperability between different blockchains while providing specialized functionality tailored to specific use cases. Think of them as specialized, custom-built chains created for specific use cases, such as Web3 gaming or DeFi trading.
Key Features of Layer-3 Networks
Layer-3 networks offer distinct advantages that set them apart from their predecessors:
Enhanced Scalability and Efficiency
By optimizing consensus mechanisms and data structures, Layer-3 networks achieve higher transaction throughput and processing capabilities. This allows decentralized applications (dApps) to perform with extreme efficiency, minimizing network congestion and computational bottlenecks.
Improved Interoperability and Accessibility
One of the key benefits of Layer-3 networks is their ability to seamlessly communicate and transfer assets between different blockchains. This interoperability means the crypto ecosystem becomes more connected and more accessible, enabling users to navigate and bridge across various networks with ease and far less risk.
Customization and Security
Layer-3 networks usually host only one dApp per network. This allows developers to customize their chains to their satisfaction, and implement security features tailored specifically to their dApp’s requirements. By providing a dedicated environment for each application, Layer-3 networks ensure optimal performance and enhanced security.
Notable Layer-3 Projects
Several promising Layer-3 projects have emerged, each bringing its own set of innovative features and use cases to the table.
Orbs
Orbs positions itself as a Layer-3 infrastructure project, bridging the gap between Layer-1, Layer-2, and the application layer. By providing an intermediary execution layer, Orbs enhances smart contract capabilities and introduces groundbreaking DeFi protocols such as dLIMIT, dTWAP, and Liquidity Hub.
Degen Chain
Built on the Base blockchain, Degen Chain is a Layer-3 platform designed to efficiently handle payment and gaming transactions. With its thriving ecosystem of tokens and rapid growth, Degen Chain aims to tackle scalability issues while maintaining low transaction costs.
Social media influencers have relentlessly shilled the chain in recent weeks for potential airdrops, and attracted a lot of investment as a result.
Arbitrum Orbit
Arbitrum Orbit enables developers to create customizable Layer-2 or Layer-3 chains within the Arbitrum ecosystem. These chains can settle transactions on Arbitrum One, providing developers with the flexibility to tailor their application’s features and governance to their specific needs.
Other notable Layer-3 projects include Cosmos IBC, Polkadot, Chainlink, Superchain, and zkHyperchains, each contributing to the evolution of the blockchain landscape in their own unique ways.
Potential Impact and Use Cases
Layer-3 networks hold immense potential for the future of blockchain technology. Here are a few of the biggest plusses.
Decongesting the Main Chain
By processing transactions off-chain, Layer-3 solutions help alleviate congestion on the main blockchain. This leads to reduced network congestion and lower transaction fees, improving the overall user experience.
Enabling Complex dApps
The specialized functionality offered by Layer-3 networks opens up new possibilities to develop sophisticated and user-friendly dApps across sectors like DeFi, gaming, and social media. By providing a tailored environment for each application, Layer-3 networks enable developers to create highly optimized and efficient dApps.
Driving Mainstream Adoption
The ability to create customized, high-performance applications lowers the entry barrier for businesses and individuals, fostering a more inclusive and diverse crypto ecosystem.
Challenges and Considerations
While Layer-3 networks present exciting opportunities, they also face certain challenges that need to be addressed.
Centralization Concerns
Some critics argue that Layer-3 networks, being built on top of potentially centralized Layer-2 solutions, may further compromise the decentralization principles that is the soul of blockchain technology. Striking the right balance between scalability and decentralization remains a crucial consideration for Layer-3 networks.
Competition and Fragmentation
As more Layer-3 networks enter the fray, competition for users and developers is likely to intensify. This could lead to fragmentation within the crypto ecosystem, with liquidity and resources being spread across multiple platforms. Ensuring a cohesive and interconnected ecosystem will be a key challenge for Layer-3 networks.
Conclusion
Layer-3 networks can make blockchain technology. By building upon the foundations laid by more scalable, interoperable, and specialized than ever before. As the crypto landscape continues to mature, Layer-3 networks are poised to play a crucial role in shaping its future.
For beginners navigating the complex world of cryptocurrencies, understanding the significance of Layer-3 networks is essential. By staying informed about these cutting-edge developments, individuals can position themselves to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this next-generation technology.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, Layer-3 networks will undoubtedly face challenges and obstacles. However, the potential benefits they offer in terms of scalability, interoperability, and specialized functionality are too significant to ignore. As more projects emerge and mature, the true impact of Layer-3 networks will become increasingly apparent.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)






2 Comments
2 thoughts on “Layer-3 (L3) Networks: Climbing Crypto’s Next Frontier”
This was informative.
🟨 😴 😡 ❌ 🤮 💩
nice
🟨 😴 😡 ❌ 🤮 💩