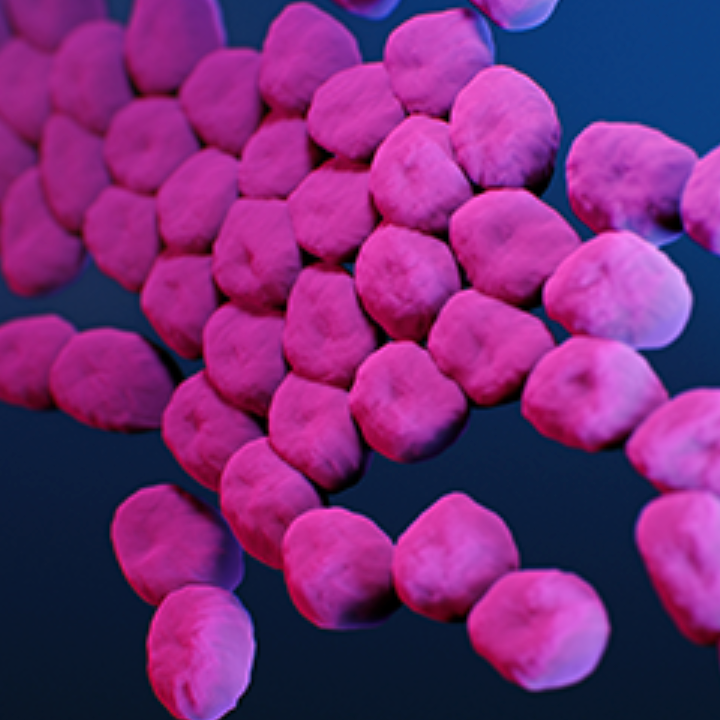
Acinetobacter is a group of bacteria commonly found in the environment. The most common cause of infections is Acinetobacter baumannii. (credit: CDC)
Researchers at Stanford Medicine and McMaster University have devised a new AI model, SyntheMol (“synthesizing molecules”), which creates recipes for chemists to synthesize drugs in the lab. With nearly 5 million deaths linked to antibiotic resistance globally every year, new ways to combat resistant bacterial strains are urgently needed, according to the researchers.
Using SyntheMol, the researchers have so far developed six novel drugs aimed at killing resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii, one of the leading pathogens responsible for antibacterial resistance-related deaths, as noted in a study published March 22 in the journal Nature Machine Intelligence.
25,000 possible antibiotics and the recipes to make them in less than nine hours
The model was trained to construct potential drugs using a library of more than 130,000 molecular building blocks and a set of validated chemical reactions. It generated the final compound and the steps it took with those building blocks, giving the researchers a set of recipes to produce the drugs.
The researchers also trained the model on existing data of different chemicals’ antibacterial activity against A. baumannii. With these guidelines and its building block starting set, SyntheMol generated around 25,000 possible antibiotics and the recipes to make them in less than nine hours.
To prevent the bacteria from quickly developing resistance to the new compounds, researchers then filtered the generated compounds to only those that were dissimilar from existing compounds.
“Now we have not just entirely new molecules but also explicit instructions for how to make those molecules,” said James Zou, PhD, an associate professor of biomedical data science and co-senior author on the study.
A new chemical space
The researchers chose the 70 compounds with the highest potential to kill the Acinetobacter baumannii bacterium. The company was able to efficiently generate 58 of these compounds, six of which killed a resistant strain of A. baumannii when researchers tested them in the lab. These new compounds also showed antibacterial activity against other kinds of infectious bacteria prone to antibiotic resistance, including E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and MRSA.
The scientists were able to further safety-test two of the six compounds for toxicity in mice. The next step is to test the drugs in mice infected with A. baumannii to see if they work in a living body,” Zou said. “This AI is really designing and teaching us about this entirely new part of the chemical space that humans just haven’t explored before.”
The study was funded by the Weston Family Foundation, the David Braley Centre for Antibiotic Discovery, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, M. and M. Heersink, the Chan-Zuckerberg Biohub, and the Knight-Hennessy scholarship.
Citation: Swanson, K., Liu, G., Catacutan, D.B. et al. Generative AI for designing and validating easily synthesizable and structurally novel antibiotics. Nat Mach Intell 6, 338–353 (2024). https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-024-00809-7
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)