Simple synthetic cells produce and transfer energy like natural cells
Oct. 22, 2024.
2 mins. read.
9 Interactions
Scientists are trying to create synthetic cells that are simplified versions of living cells and work like living cells.
Scientists at the University of Groningen are trying to create synthetic cells that are simplified versions of living cells and work like living cells.
The scientists have successfully replicated the natural process of energy production and transfer in living cells.
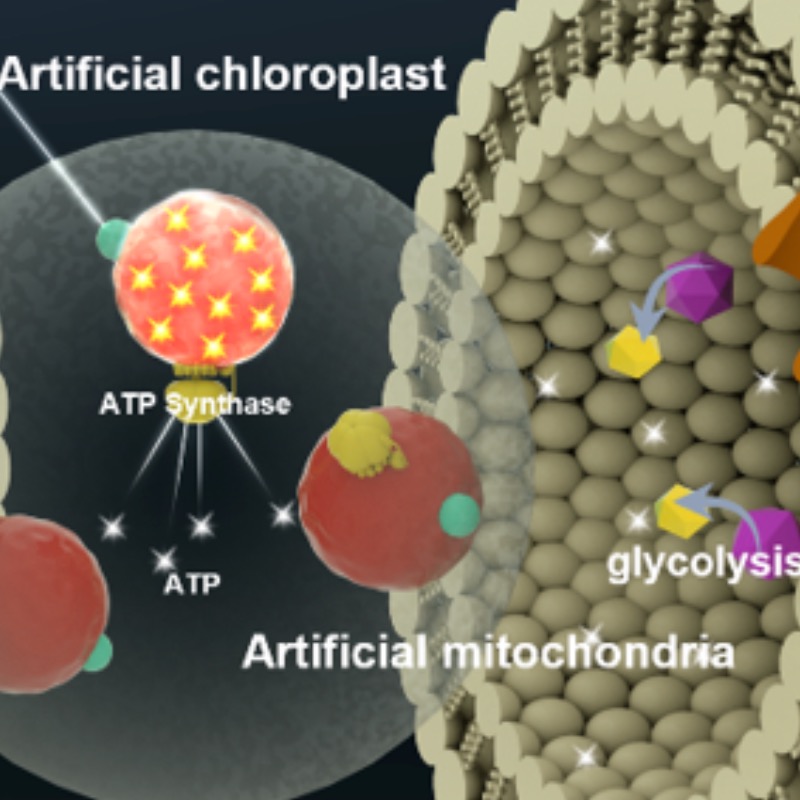
Mitochondria, the “energy factories” of cells, produce energy in the form of a molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), which is the main energy carrier in cells.
ATP stores and supplies the energy needed for many cellular processes. The ATP molecule becomes ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) after releasing its energy. ADP can be converted back into ATP.
The scientists have used only five components to produce ATP, compared to the hundreds used by natural mitochondria. They placed the simplified system inside vesicles, small sacs that can carry substances within a cell or between cells.
These vesicles can absorb ADP and an amino acid called arginine from their surroundings. Burning arginine provides energy and converts ADP back into ATP.
Another type of vesicle can absorb the ATP produced and use it for energy-consuming reactions, turning ATP back into ADP, which can then be reused by the first vesicle. This cycle mimics the natural process of energy production and use in cells.
The scientists have described their research methods and results in two research papers.
In the first paper, published in Nature Communications in September, they have described a system for energy conversion and cross-feeding of products of this reaction between synthetic cells.
In the second paper, just published in Nature Nanotechnology, they have described a system for concentrating and converting nutrients in cells.
Applications and future research
Understanding how to create synthetic cells can help scientists learn more about the fundamental processes of life. It can also lead to new technologies in medicine and biotechnology.
“Ultimately, this would give us a blueprint for life, something that is currently lacking in biology,” says research leader Bert Poolman. “This may eventually have all kinds of applications, but will also help us to better understand what life is.”
This seems a small step to replicate some important cellular processes in synthetic cells. But eventually, research on synthetic cells could lead to the ability to engineer entire living beings.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)



0 Comments
0 thoughts on “Simple synthetic cells produce and transfer energy like natural cells”