Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.
Web3 Wars: GameFi Dapps Overtaken By Crypto AI Growth, What’s Next?
TL;DR
- AI Dapps now have 28% of blockchain activity, surpassing GameFi Dapps at 26%
- GameFi is still growing: 4 million daily active wallets, up 79% month-over-month.
- Q2 2024 saw $1.1 billion investment in blockchain gaming; July dropped significantly.
Introduction
Blockchain’s decentralized application (Dapp) industry has witnessed a significant shift in recent months, with artificial intelligence (AI) Dapps surpassing crypto gaming (GameFi) Dapps as the leading category for the very first time.
This development, highlighted in the July 2024 DappRadar Games Report, means that gaming remains a robust and growing sector, but that AI-powered Dapps are the hotter current tech trends, and hold a bit more mindshare in the space right now.
AI Dapps Take the Lead
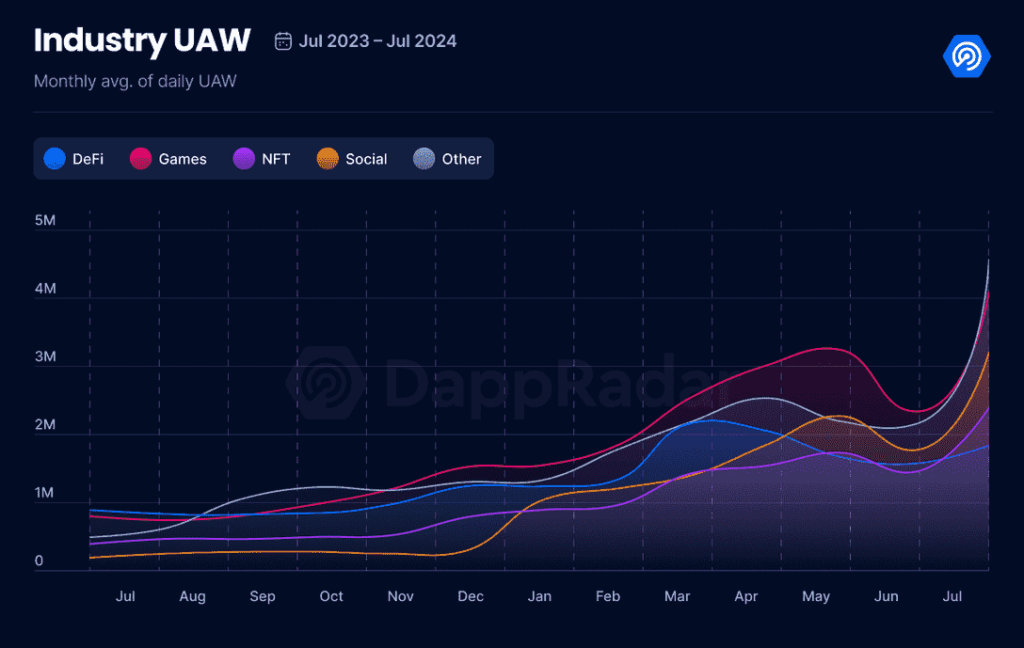
- In July 2024, the Dapp industry maintained its impressive milestone of over 15 million daily unique active wallets (dUAW) interacting with blockchain applications.
- However, the most striking development was the rise of DappRadar’s ‘Other’ category, which primarily consists of AI-based Dapps, to the top position with a 28% share of user activity.
- Gaming Dapps still demonstrated significant growth.The sector now represents 26% of DApp activity, engaging 4 million dUAW – a remarkable 79% increase from the previous month.
The rise of AI Dapps reflects a broader trend in the tech industry, where artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into sectors from finance to entertainment. In the blockchain space, AI applications are leveraging decentralized networks that provide services from decentralized AI computations by projects like Render to AI-driven data analysis and prediction markets.
Gaming Sector Plays On
Despite being overtaken by AI Dapps, the blockchain gaming sector continues to show strength and innovation. The report highlights several key developments and trends:
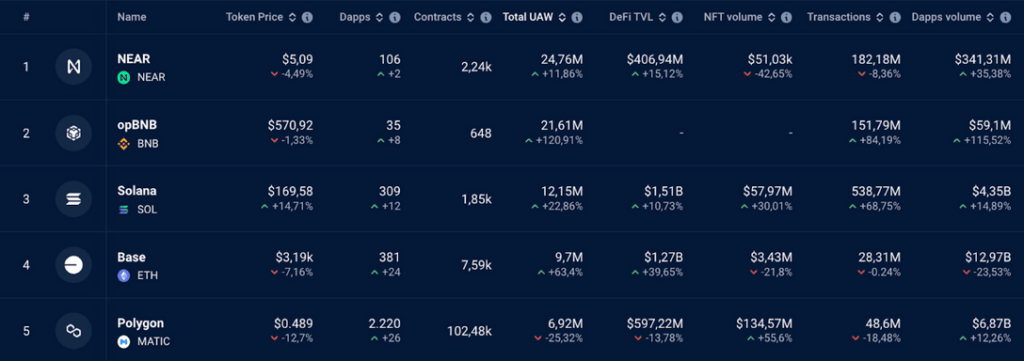
1. Blockchain Diversity: Ronin remains the leading blockchain for gaming activity, driven by popular titles like Pixels and Lumiterra. Other networks like opBNB, Oasys, NEAR, and Immutable zkEVM are also seeing significant engagement, showcasing the diverse ecosystem of blockchain gaming platforms.
2. Emerging Titles: New games like SERAPH: In the Darkness, which launched in mid-July, have quickly gained traction, indicating ongoing innovation and user interest in fresh gaming experiences.
3. NFT Trading: Despite a general decline in metaverse-based NFT collections, gaming NFTs continue to see active trading. Gods Unchained and Axie Infinity remain the most traded gaming NFT collections, while newer entries like Guild of Guardians are gaining popularity.
4. Cross-Platform Integration: The success of games published on major platforms like the App Store and Epic Games Store shows the growing acceptance of blockchain and NFT elements in mainstream gaming channels.
Investment Landscape
The investment climate for blockchain gaming and metaverse projects is a mixed picture. July 2024 saw the lowest investment level since Q3 2020 – just $23 million across three deals – but the preceding quarter (Q2 2024) was notably strong.
Q2 marked the best quarter for blockchain gaming investments since Q3 2022, with $1.1 billion raised – a 314% increase from the previous quarter.
Key investments in Q2 included:
1. a16z Gaming Fund: Raised $600 million for game studios, infrastructure, and the Games x Consumer ecosystem.
2. Bitkraft Venture Fund: Secured $275 million for early-stage investments in gaming and interactive media companies.
3. Metaverse Projects: Significant investments in Baby Shark Universe ($34 million) and The Sandbox ($20 million) demonstrate ongoing interest in metaverse development.
These investments, focused on infrastructure and foundational development, suggest a strategic approach to enriching the Web3 gaming ecosystem. The contrast between the robust Q2 and the subdued July may indicate a temporary summer lull rather than a long-term trend.

GameFi Q2 Industry Snapshot and Analysis
1. User Engagement: Blockchain games remain strong in the Web3 industry, accounting for 26% of all Dapp activity and attracting 2.8 million active wallets daily. This persistent engagement suggests that gaming remains a key driver for Web3 adoption.
2. Blockchain Performance: Ronin has reclaimed the top spot among gaming blockchains, with a 100% increase to 1.9 million dUAW. This indicates the Ronin platform has strong user appeal. Newer platforms like Immutable zkEVM and opBNB grow rapidly.
3. Game Performance: Pixels leads the gaming landscape with 48 million unique wallets this quarter, demonstrating the enduring appeal of well-established titles. The success of newer entries like Guild of Guardians, especially following their mobile launch, shows the potential for growth through strategic platform expansions.
4. Metaverse Developments: Metaverse-based NFT collections saw a 29% decline in trading volume and a 21% drop in sales. Projects like Animoca Brands’ Mocaverse continue to dominate, capturing half of the trading volume. This suggests that while the metaverse concept may be experiencing reduced hype, established projects are maintaining their market positions.
5. Technological Advancements: The industry continues to focus on seamless gameplay experiences, investing in infrastructure and cross-chain compatibility. This focus on user experience is crucial to acquire and retain users.
6. Friend or Foe? The rise of AI Dapps presents both a challenge and an opportunity to GameFi. Gaming developers may need to integrate AI elements to stay competitive, potentially leading to more sophisticated and engaging gameplay experiences.
Looking Ahead
Despite the challenges, the blockchain gaming industry shows promising signs for future growth, especially if the 2024/2025 crypto bull run gets back on track.
New game launches are succeeding, and lots of blockchain platforms are getting traction. These trends show continuing innovation in tech, in gameplay, tokenomics, and user engagement strategies. There is potential crossover with traditional gaming platforms (as we’ve seen with Gunzilla and PS5), and interest from established tech companies. Broader industry collaborations will help the GameFi industry scale beyond what we’ve seen.
Significant investments in gaming funds and infrastructure projects continue to lay the groundwork for more sophisticated and scalable blockchain gaming experiences. Also, the rise of AI Dapps may lead to innovative hybrid models, combining elements of AI and gaming to create new, engaging experiences for users.
The rise of AI Dapps presents both a challenge and an opportunity for the GameFi sector to evolve and integrate new technologies. The capital is there. Substantial investments in Web3 gaming, infrastructure, emerging platforms, and cross-industry collaborations are laying the foundations for an exciting next phase of blockchain gaming evolution.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.
What Will You Do With Your Digital Twin? | AGI 24 Series – Part 1
Finally! ProofMode Can Create Verified Photo and Video Evidence: Dweb Series – Part 2
Combining Knowledge Graphs and Large Language Models
Introduction
The growing interest in integrating Knowledge Graphs (KGs) and Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications is large. LLMs, such as BERT, GPT, and T5, have achieved state-of-the-art performance in various NLP tasks but still exhibit limitations, such as generating hallucinations (false information) and lacking domain-specific knowledge. KGs, on the other hand, provide structured and accurate information about entities and their relationships, which can complement LLMs’ capabilities. Even though LLMs are powerful NLP models trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human language, they sometimes produce incorrect or nonsensical information, especially in domain-specific contexts.
So what are KGs and how can they improve LLMS? Knowledge Graphs (KGs): are databases that represent information in a structured format, with entities (nodes) connected by relationships (edges). They capture the semantics and interconnections between entities, making them valuable for enhancing the factual accuracy and domain knowledge of LLMs.
Methods for Enhancing LLMs with KGs
- Knowledge Injection: KAPING (Knowledge-Augmented Pre-trained Language Models) and DRAK (Dynamic Relational Attention Knowledge) are techniques that inject factual knowledge from KGs into LLMs to provide context and improve performance in tasks like zero-shot question answering. This helps LLMs generate more accurate and relevant responses by leveraging structured knowledge.
- Example: Injecting information about medical conditions and treatments from a medical KG into an LLM to improve its performance in medical question-answering tasks.
- Increasing Explainability: Methods like QA-GNN (Question Answering with Graph Neural Networks) and LMExplainer integrate KGs with LLMs to provide better interpretability and reasoning paths for the model’s outputs. By incorporating KGs, these methods can trace back the sources of information and explain how a particular answer was derived.
- Example: Using a KG to provide reasoning paths for answers generated by an LLM, making it easier to understand the logic behind the model’s responses in a legal context.
- Semantic Understanding: Approaches like LUKE (Language Understanding with Knowledge-based Embeddings) and R3 (Relational Reasoning for Reading Comprehension) enhance LLMs by adding semantic understanding and entity embeddings from KGs. This allows LLMs to better comprehend the relationships between entities and generate more coherent and contextually appropriate responses.
- Example: Enhancing an LLM with embeddings from a geographic KG to improve its understanding of geographical entities and relationships in tasks like location-based question answering.
Methods for Enhancing KGs with LLMs
- Temporal Forecasting: LLMs are used to predict future facts in Temporal Knowledge Graphs (TKGs) by understanding the semantic meaning of entities and relationships over time. This helps in forecasting events and trends based on historical data stored in KGs.
- Example: Using an LLM to predict future business trends by analyzing historical data on company performances and market conditions stored in a TKG.
- Knowledge Graph Construction: LLMs assist in the construction of KGs by performing tasks like relation extraction, entity recognition, and property identification. This automates the process of building and updating KGs, making it more efficient and accurate.
- Example: Using an LLM to extract relationships between scientific concepts from research papers and incorporate them into a scientific KG.
Brief Thematic Analysis
There is a complementary relationship between KGs and LLMs, and their integration can significantly improve the performance and trustworthiness of AI applications. The key themes include:
- Accuracy and Reliability: Integrating KGs with LLMs improves the factual accuracy and reliability of the models by providing structured and verified information.
- Explainability and Interpretability: Methods that combine KGs and LLMs enhance the explainability of model outputs, making it easier to understand and trust the generated information.
- Efficiency and Automation: Using LLMs to construct and maintain KGs automates the process, reducing the time and effort required for manual updates.
Conclusion
The integration of KGs and LLMs offers a promising approach to addressing the limitations of LLMs and enhancing the capabilities of KGs. It is a discussion of current and future challenges in this field, providing insights for researchers and practitioners interested in this area. The key takeaways include:
- Mutual Benefits: KGs provide structured and domain-specific knowledge to LLMs, reducing hallucinations and improving accuracy, while LLMs enhance the construction and updating of KGs, making the process more efficient.
- Research Directions: Future research should focus on developing more sophisticated methods for integrating KGs and LLMs, addressing challenges such as scalability, dynamic updates, and context awareness.
- Practical Applications: The integration of KGs and LLMs has significant implications for various NLP applications, including question answering, information retrieval, and knowledge management.
Key Points
- Knowledge Injection: Techniques like KAPING and DRAK use KGs to provide additional context and facts to LLMs, improving their performance in tasks such as zero-shot question answering.
- Explainability: Methods like QA-GNN and LMExplainer integrate KGs with LLMs to provide better interpretability and reasoning paths for the models’ outputs.
- Semantic Understanding: Approaches like LUKE and R3 enhance LLMs by adding semantic understanding and entity embeddings from KGs.
- Temporal Forecasting: LLMs are used to predict future facts in Temporal Knowledge Graphs (TKGs) by understanding the semantic meaning of entities and relationships over time.
- KG Construction: LLMs assist in the construction of KGs by performing tasks like relation extraction and property identification, making the process more automated and accurate.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.
This New AI-Enabled Biometric System Could Change Retail Forever: Super AI Series – Part 8
Ten books to read to understand technology and change
Looking for a guidebook to help you navigate our changing world?
Has the pace of change in the 21st century got you disorientated?
Let me draw your attention to ten books I’ve read recently. They each deal with the development of technology in the present and the near future, and its effects on society. Each of them are eye-opening and thought-provoking in their own ways. Indeed, they might change your life path, so beware!

1) Power, Sex, Suicide: Mitochondria and the meaning of life. By Nick Lane.
Fascinating account of the remarkable (and unlikely) evolutionary journey from non-life to modern warm-blooded life. With plenty of insights along the way regarding energy, sex, aging, and death. You’ll wonder why you never knew about this before.
2) Methuselah’s Zoo: What nature can teach us about living longer, healthier lives. By Steven Austad.
A different view regarding what animals can teach us about aging. Many animals live longer, healthier lives than any simple theory would predict – this book explains why and considers the implications for human aging, and for what kind of studies rejuvenation researchers should prioritize.
3) Eve: How the female body drove 200 million years of human evolution. By Cat Bohannon.
Milk. The womb. Menopause. Perception. Tools. Voice. The brain. Love. When you look at the long span of evolution from a female perspective, many things fall into place in an inspiring new way. A welcome reminder that our approach to science often suffers from being male-centric.
4) We Are Electric: The new science of our body’s electrome. By Sally Adee.
A look at biology from a fascinating alternative angle. The electricity throughout our bodies is involved in more processes than we previously thought. Move over genome, epigenome, and biome: make way for the electrome.
5) Sentience: The invention of consciousness. By Nicholas Humphrey.
Why did evolution give rise to phenomenological consciousness? How can we detect and assess consciousness throughout the animal kingdom? And what are the implications for AIs that might be sentient? Lots of captivating biographical asides along the way.

6) The Other Pandemic: How QAnon contaminated the world. By James Ball.
Evolution has produced not just intelligence and beauty but also viruses and other pathogens. Mental pathogens (‘memes’) have lots in common with their biological analogues. That’s one reason why the whole world may be on the point of going crazy.
7) The Deadly Rise of Anti-Science: A scientist’s warning. By Peter Hotez.
Part of the growing wave of social irrationality is a determined virulent opposition to the patient methods and hard-won insights of science. Millions have already died as a result. There may be worse ahead. What lies behind these developments? And how can they be parried?
8) End Times: Elites, counter-elites, and the path of political disintegration. By Peter Turchin.
Can we ever have a science of history? Is that idea a fantasy? This book argues that there are important patterns that transcend individual periods of revolutionary turmoil. However, there’s no inevitability in these patterns, provided we are wise and pay attention. You’ll never look at history the same way again.
9) The Coming Wave: Technology, power, and the 21st century’s greatest dilemma. By Mustafa Suleyman.
Current debates about the safety of powerful AI systems should be understood in wider context: economic, political, and historical context. Following a full diagnosis, a ten-stage multi-level plan provides some grounds for optimism.
10) Uncontrollable: The threat of artificial superintelligence and the race to save the world. By Darren McKee.
Will powerful AI systems pose catastrophic risks to humanity? Are you, as an individual, helpless to reduce these risks? Read this book to find out. Written compellingly, with particular clarity.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.
A Paean for Privacy and the Accidental Authoritarian Tomorrow
I lost my phone the other day. I retraced my steps around town before giving up and going home – where I could fire up Google on my laptop and quickly locate the device. Not just to a local area, but to the exact hedgerow where it had fallen out of my pocket – right down to the individual shrub. Blessed be! With a quiet and fervent prayer of thanks to Google, I got on with my day – safe in the knowledge Google was tracking every movement I made.
It didn’t take long for my gratitude to turn sour. Of course, I’ve known all along: Google can track me. Law enforcement have been pinging cell towers to track suspects since the 1990s. Yet something about the precision strike on my location felt different. Google doesn’t just know what block I’m on – it knows which couch I’m sitting on.
The End of Individual Freedom
It’s not just Google. An industry handles the data that Google collects, and it’s shared with the government and military under the PRISM project. It’s hard to have any faith that SHA-256 encryption or and Google’s cybersecurity practices mean our data is only handled in just and proper ways. Only recently the company deleted an entire pension fund. Oops.
This is not a polemic against Google, they’re just a useful example. Surveillance capitalism powers most major tech corporations, their market cap riding on the data they process and harvest every centisecond: location data, online interactions, and creepy psychological profiles based on that.
When I praised the ability to find my device, glad that Google was watching, I exemplified the attitude of consumers who have for decades now ceded autonomy to zaibatsus in exchange for the services they provide. Yet the relentless data breaches, lawsuits, and system outages are starting to make society question, rightly, how senseless this ultimately was.
Are you comfortable having your preferences tracked to have good and appropriate products advertised to you? Are you any naturally less comfortable with the idea of major corporations being able to construct a better profile of you than your psychotherapist could? Privacy is now a battleground of the individual against the corporation. Our future society depends on the battle.

Wiretapped
You – dear reader – no longer have the right, or indeed the ability, to protect your personal privacy. Google quite literally knows more about you than your family and friends do. After all, does your husband or wife know where you are all the time? And if they had the ability to find out, how comfortable would you be if they kept on tracking you? Probably not; you’d probably file for divorce. Google – and their NSA partners – already know. As would anyone who hacked their systems, or any Google employee with the right access.
This spectre of panoptic rule by corporations is somewhat diluted by the sheer weight of information we produce. It takes sophisticated algorithms to rapidly index the copious amounts of information being vomited forth every second and make it, as per Google’s credo ‘organised and accessible’. Without the AI, invasions of privacy would have to be tailored, slowing our corporate adversaries. However, the advent of LLMs, AIs, better data indexing tools, and ever more sensory equipment dotted around thanks to the “Internet of Things’ – such complete intrusive oversight of our lives, all our lives, is on the verge of complete reality.
“The USA Patriot Act of 2001 authorized unprecedented surveillance of American citizens and individuals worldwide without traditional civil liberties safeguards” – it was a scandal at the time and it’s gotten so much worse since. The size, scale and sense that our lives are being recorded has only grown. Do you really believe Alexa isn’t listening? Do you think that our phones are not recording? Do you think Microsoft bought Discord because of the revenue it generates? Many people have had the Baader Meinhof effect where they talk to a friend about an anime series and then see merchandise for that series advertised to them. If that’s happened to you I am sorry to say you’ve been wiretapped.
Authoritarian Angst
We’ve all been wiretapped. Constantly. For years. We broadly put up with it with various excuses: “the data I produce isn’t actionable”, “the NSA wouldn’t do anything bad with it”, “we need to stop terrorists”. But the truth – practically and neurologically – is that we addicted to the devices that surveil us. The rise of AI means all that data is actionable. An interviewer will pay a tech corporation for an online profile of you for every job you apply to, and have an LLM review all your recent online activity for red flags. A bank may refuse you a loan because your phone location went to the casino twice this month. Police may visit you if your political leanings are suspect.
This is just the tip of the authoritarian spear. Western propaganda points fingers at China as a fearful vision of an authoritarian future, where facial recognition is common. But do they realise the megacorps of mostly the USA that are architected modern digital surveillance? I am delighted that you found my phone, Google – all it cost me was everything. It is essential to restore privacy to technology, and to create systems where the user controls their data, their applications and their devices – but I fear we may be too late.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.
Is The Era of Generative AIs Already Over?
As Wall Street begins to call AI’s bluff, have GPTs to date delivered a ‘killer app’?
First, excitement. Then, fear. Then boredom? Generative AIs and LLMs burst onto the scene with considerable fanfare. It wasn’t long before prophets of doom began declaring the end times for late-stage capitalism and the beginning of techno-fiefdoms that would take our jobs and remake our societies – for better or for worse.
Venture capital sent waves of backing to AI startups desperate to seize a piece of the new frontier for themselves. Formerly a niche interest of nerds who had taken psychedelics and saw the machinery of the mind, AI became the marketing buzzword, draping itself seductively over every sector in the economy.
The future, and the end, was nigh. Intellectual automation was on the brink of world dominion. No job was safe, no social structure secure – and what happened next would define the rest of our lives.
Except perhaps, it wouldn’t. Perhaps – unlike the PC, smartphones and social networks that were Big Tech’s last great inventions – LLMs and generative AI are struggling to move the needle quite the way we expected. Wall Street started to panic, and soon after so did everyone else. CEOs who had replaced parts of their workforce with GPT were suddenly wearing shocked pikachu faces that the output didn’t have consistent quality, and that customers do not like the feeling of being served by a machine.
We’ve had decades of films, books and sci-fi to warn us about the perils of abandoning our organic agency – and seeing the first glimmers of that in our real world has been a warning, a terrifying one for some. More simply: why am I paying for a service you’ve decided a GPT can do for me? I might as well just download my own.
This isn’t to say AI hasn’t had an impact, it has. My writer friends working on the content-farm base of the pyramid have struggled, as have my musician mates who chiefly trade in jingles and ditties. Only my most talented friends in graphic design have survived so far. Many creatives hacking out at a living at the base of the pyramid are finding work harder and harder to find. To them I say: don’t worry, your time will come again. It doesn’t matter how good AI gets – it still smells like AI. And people are already turning against it. We don’t mind when it’s used for the little things, but for anything that has value to us, or anything we pay for – we want a human.

People would rather read error-strewn human-made logically inconsistent rubbish than pristine AI copy devoid of true insight. And if you’re writing technical documents. Well – someone still needs to check the LLM hasn’t hallucinated that you’re meant to cut the blue wire not the red. Accountability matters. You can’t hold a generative machine accountable for anything; it doesn’t know what it said.
Practically, the generative AI train’s wheels are also grinding to a halt. Initially, vast amounts of data were acquired, and fed to competent models, and engineers got exponential progression in ability. Now the returns are diminishing fast.
Our carbon-based neural clusters are so dense that we can discern, judge and then perform tasks we have never encountered before – and we can do it pretty damn well. We just can’t fit that many more transistors on a chip, and we can’t feed an AI more data in a whole lifetime than we absorb in a single day through our five senses. The gulf in class between us and our baby-models is too vast, no matter how much corporations with a vested interest in saving labour-costs want to convince us otherwise.
Besides, these models are expensive. Fearsomely, ridiculously expensive. Nvidia briefly overturned all its rivals trying to build bespoke corporate AIs by selling the shovels required to make them. The race for ‘compute’ is as scary as it is damaging to the bottom line. Invest now, save and earn later – that’s the basic principle of investment, but with AI the balance is completely out of whack, with trillions invested into models that, to date, have failed to deliver any sort of ‘killer app’.
Indeed, the killer app is probably already here: in the form of GPT’s ability to summarise and recapitulate difficult documentation. I’m coding a game right now – GPT is a godsend, in education as well as application. As an assistant, it’s a delight. Yet perhaps that’s where the generative AI advance ends for now. It’s a useful time-saver, and Skynet’s rise to power is still far away. White-collar workers may indeed be safe. I’ve already seen writing jobs re-emerge en masse as CEOs begin to realise their mistake. It seems that the collective AI mania has begun to abate, and by treating our new tool as just that, a handy new tool, we’ll all be much the better for it.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.
Bitcoin: These Governments Hold Billions of Dollars in BTC
New crypto poster boy Donald Trump made waves at the recent Bitcoin Nashville 2024 conference where he and other politicians unveiled plans to create a governmental ‘Bitcoin reserve’ of sorts. This bullish news came in the wake of a tough July for BTC where Germany sold off $3 billion of dollars in seized Bitcoin, pushing its price down significantly to the low $50,000s.
While Bitcoin started as a libertarian ideal which was supposed to help free Joe Public from the financial control of evil governments and their central banks, 15 years later it is clear that idealism doesn’t survive reality unharmed.
The US government now holds a staggering 200,000, and it’s not the only country to have a big bag of Bitcoin for a rainy day. Other governments around the world have found themselves in possession of significant amounts of Bitcoin (BTC) and other cryptocurrencies, which they are HODLing for whatever reason they deem fit.
These holdings are often the result of seizures from criminal activities rather than intentional investments, but that makes no difference in the end. The growing stockpile of digital assets under state control has consequences that must be considered.
Let’s look at Bitcoin holdings of several major governments, how they acquired these assets, and the potential implications for the crypto market.
United States: The Largest Government Holder of Bitcoin
According to data from blockchain analytics firm Arkham, the US government holds over 213,000 BTC, along with various other cryptocurrencies, bringing its total crypto holdings to approximately $4 billion. This makes it the largest holder of bitcoin among governments globally, accounting for about 1% of the total bitcoin supply of 21 million.
Interestingly, the US government has never directly purchased Bitcoin. Instead, its holdings are the result of seizures from illegal activities, particularly from the Silk Road marketplace, which was shut down by the FBI in 2013. The U.S. government has auctioned off a significant portion of its seized bitcoins, having sold around 195,000 bitcoins, generating approximately $366 million from these sales.
Some other notable cases include:
- The ‘Individual X’ case: An anonymous hacker stole over 69,000 BTC from the Silk Road darknet marketplace between 2012 and 2013. The hacker was apprehended in 2015 and forced to forfeit the stolen funds, going straight to the vaults of Uncle Sam.
- James Zhong’s Silk Road exploit: Zhong managed to steal more than 51,000 BTC from Silk Road using a technical exploit, which many don’t consider to be really criminal. He was caught in November 2021 after a decade on the run, which was covered in this fascinating documentary episode.
- The Bitfinex hack: In February 2022, authorities arrested Ilya Lichtenstein and his wife, Heather ‘RazzleKhan’ Morgan, for allegedly laundering almost 120,000 BTC stolen in the 2016 Bitfinex hack.
The US government typically keeps seized crypto assets in cold storage during ongoing investigations. Once cases are resolved, these assets are often converted to fiat currency through exchanges or OTC auctions. Between 2014 and 2023, the US government sold over $360 million worth of BTC across 11 different auctions.
However, if Trump gets elected, he has promised that the US government will, “Never sell your Bitcoin”.
China Plays Both Sides
Despite its bipolar attitude and well-known crackdown on cryptocurrency trading and mining, the Chinese government has also found itself in possession of a substantial amount of Bitcoin. In 2020, Chinese authorities seized over 190,000 BTC, along with other cryptocurrencies, from the Plus Token scam project. This massive haul was valued at billions of dollars at the time.
While it’s unclear if China still holds all of these assets, the government stated its intention to process the seized digital currencies “pursuant to laws” and forfeit the proceeds to the national treasury. This suggests that much of the confiscated crypto may have already been exchanged for fiat currency.
Interestingly, despite the ban on crypto mining in China, there have been speculations about state-owned mining operations. In October 2023, reports emerged of a Bitcoin mining operation called Bit Origin, which could be traced back to the Chinese government, raising questions about China’s true stance on cryptocurrency.
United Kingdom Nabs 61,000 BTC from Criminal Activities
The United Kingdom has also amassed a significant Bitcoin holding through law enforcement actions. In one high-profile case, London’s Metropolitan Police seized over 61,000 BTC from a female UK citizen named Jian Wen, who was found guilty of laundering funds from an investment fraud operation in China.
The UK government has been actively seizing cryptocurrencies used in criminal activities. In June and July 2021, the Metropolitan Police confiscated around £180 million worth of crypto assets as part of a money laundering investigation, setting new records for the largest crypto seizures in the country.
A new law that came into effect in April 2024 has given UK law enforcement agencies more power to seize, freeze, and destroy cryptocurrency used by criminals. This legislation is likely to cause even more crypto assets to come under government control in the future.
Ukraine Mixes Government and Official Holdings
Ukraine presents an interesting case in the realm of government Bitcoin holdings. The country has received significant crypto donations to support its war effort, with estimates suggesting over $225 million raised by July 2023. But it’s the holdings of government officials that truly stand out.
In April 2021, a Ukrainian government data report revealed that public officials owned over 46,000 BTC, worth $2.67 billion at the time. Out of 700,000 officials who made property declarations, 652 declared Bitcoin ownership, with an average holding of 71 BTC each. Some officials reported owning over 5,000 BTC, with one claiming ownership of 18,000 BTC – worth over $1.1 billion at current prices.
El Salvador Continues to Accumulate
And of course, this article would be remiss to not mention El Salvador. Under its leader Nayib Bukele, the country became the first to adopt bitcoin as legal tender in September 2021 to much fanfare at the Bitcoin Miami conference. El Salvador was mocked at first for its meager holdings and took even more flak during the 2022 bear market, but with Bitcoin’s dramatic reversal of fortune in 2023, its investment has come up roses ever since.
El Salvador currently holds approximately 5,770 bitcoins, valued at around $340 million as of August 2024. This makes it one of the largest government holders of bitcoin globally.

Potential Market Impact and Future Outlook
These big Bitcoin holdings by governments raise a question: what impact can this have on the crypto market? Some come from seizures, some from intentional investments, but either represent a substantial amount of Bitcoin that could potentially enter the market.
Government sales of Bitcoin, such as the recent German government sell-off, give Supply a shot-in-the-arm in its neverending armwrestle against Demand, pushing prices downwards. Such sales also have an indirect effect: generating uncertainty among investors who are worried about the downward pressure of a sudden big sell-off.
Looking ahead, there are several factors that could further influence government attitudes towards Bitcoin:
- Regulatory developments: As crypto regulations get more cohesive worldwide, governments may gain more clarity on how to handle their holdings.
- Reserve currency potential: Some crypto pundits love to speculate that governments could eventually view Bitcoin as a potential reserve currency, especially given recent recommendations of allowing central banks to hold up to 2% of their reserves in crypto starting January 1, 2025.
- Political shifts: Changes in government leadership, such as the potential return of a crypto-friendly administration in the United States under Trump, could lead to more positive policies towards the crypto industry.
- Mining operations: Governments might opt to mine Bitcoin rather than buy it, potentially following China’s alleged model of state-owned mining operations. This will require extensive resources though, and with the recent Halving making it more expensive to mine the currency, it could be tough to get approved.
Conclusion
The world’s governments becoming significant Bitcoin holders still isn’t standard practice. But government Bitcoin holdings – even if primarily through seizures – is a growing trend, and an intriguing development in the cryptocurrency landscape.
Add to this the slow but steady accumulation of BTC through a number of spot ETFs led by TradFi giants like BlackRock, and it’s clear that Bitcoin is really starting to reach its ‘digital gold’ end-state. What these governments and Wall Street giants do with their holdings, and the power this gives them over the world’s premier digital asset, remains to be seen.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.









.png)
.png)


.png)