Introduction
The cryptocurrency industry faced significant security challenges in Q2 2024 – and it failed some. Let’s look at the latest reports from the two leading crypto security firms: Immunefi and Hacken. The analyses paint a concerning picture of the current landscape, highlighting both familiar vulnerabilities and emerging trends. Data reveals a substantial increase in successful attacks which raises alarm bells about the need for improved security measures across the crypto ecosystem.
Overview of Q2 2024 Losses
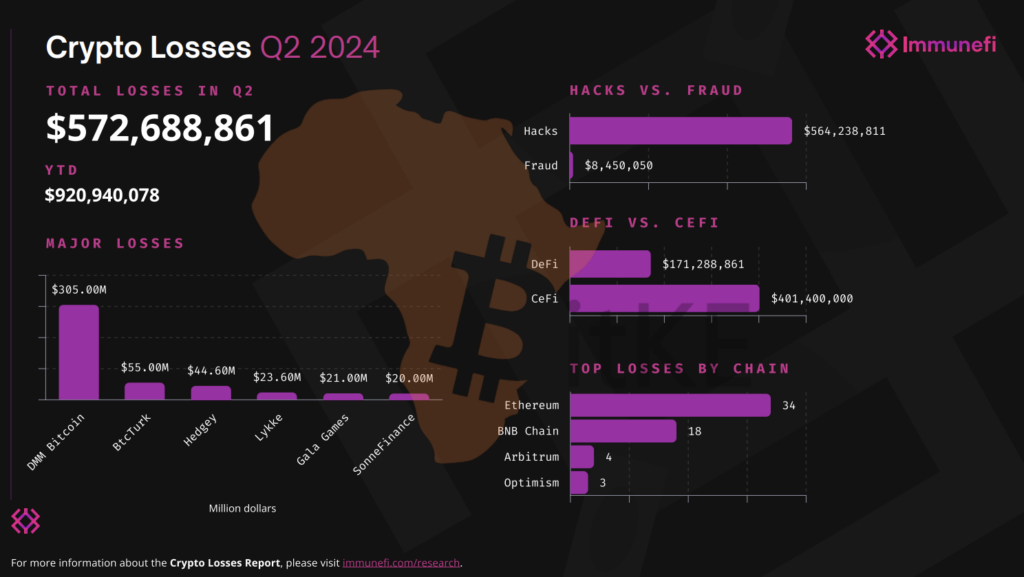
According to Immunefi, Q2 2024 saw a staggering $572.7 million lost to hacks and frauds across 72 incidents, representing a dramatic 112% increase compared to Q2 2023. Hacks continued to be the predominant cause of losses in the crypto space, with the vast majority of funds stolen through direct exploits rather than frauds or scams. This can be attributed to less awareness when markets trend upwards, which make it easier for bad actors to exploit newer users and stretched protocols.
Major Incidents
Two major incidents stood out in Q2, accounting for over 60% of total losses. The largest hack targeted DMM Bitcoin, a Japanese crypto exchange, resulting in a massive $305 million theft. This was followed by an attack on BtcTurk, Turkey’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, which suffered a $55 million loss in a cyberattack. These high-profile incidents highlight the potential vulnerabilities in even well-established exchanges and the devastating impact of successful attacks.
Shift in Attack Focus: CeFi vs. DeFi
Q2 2024 saw a significant shift in attacker focus, with Centralized Finance (CeFi) platforms bearing the brunt of attacks. CeFi losses totaled $401.4 million, accounting for 71% of all funds lost. This marks a massive 984% increase compared to Q2 2023. In contrast, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms saw a 25% decrease in losses compared to the same period last year. This shift suggests that attackers may be finding centralized platforms to be more lucrative targets, possibly due to larger pools of concentrated funds.
Most Targeted Chains
Ethereum and BNB Chain remained the primary targets for attackers, with Ethereum suffering 34 incidents and BNB Chain experiencing 18.
Arbitrum, a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum, came in third with four incidents.
Ethereum’s dominance as the most targeted chain highlights the ongoing need for heightened security measures in its ecosystem, especially as its total value locked (TVL) has grown significantly over the past year.

The types of attacks employed by malicious actors varied, but access control issues caused the highest losses at $397.2 million. Price oracle issues and flash loan attacks also contributed significantly to the overall losses. This breakdown helps identify areas where security measures need to be strengthened across the industry, providing valuable insights for both developers and security professionals.
Comparison to Previous Periods
The big increase in losses from Q2 2023 to Q2 2024 is worrying, especially considering the growth in total value locked across the crypto ecosystem. While the overall DeFi TVL tripled from about $50 billion to $150 billion by June 1, losses grew even faster.
It’s worth noting that despite fewer individual hacks compared to Q1 2024, the severity and financial impact of Q2’s attacks were significantly higher, indicating a trend towards more sophisticated and damaging exploits.
Implications for the Industry
The major hacks targeting CeFi platforms highlight the need for enhanced security measures in centralized systems. As the crypto ecosystem grows, maintaining security becomes increasingly challenging, and it will get worse if and when the 2024/2025 bull market returns. Projects must balance the desire for rapid growth with the need for robust security measures.
The industry may need to develop more comprehensive insurance solutions and standardized recovery protocols to soften the blows dealt by large-scale hacks. Additionally, these high-profile incidents may lead to increased regulatory scrutiny, potentially resulting in stricter oversight of crypto platforms, especially centralized exchanges.
Security Measures and Best Practices
Given the persistent threat of hacks and exploits, individual users and investors should take proactive steps to secure their assets. Some essential measures include:
- Using hardware wallets for long-term storage
- diversifying holdings across multiple platforms,
- enabling two-factor authentication
- staying informed about the latest security best practices
By adopting these proactive steps, users can significantly reduce their risk exposure in the face of evolving security threats.
Positive Developments
Despite the concerning trends, there’s some good news in crypto security. The industry is showing an improved ability to recover stolen funds, with about 5% of the total losses in Q2 2024 being recovered.
This represents a slight improvement from previous quarters and demonstrates the growing capability of the ecosystem to respond to and mitigate the impact of attacks. Additionally, despite Ethereum’s TVL growing by nearly 400% year-on-year, it only suffered $8 million in losses this quarter, indicating some improvement in DeFi defenses. This resilience in the face of rapid growth is an encouraging sign for the industry.

The Importance of Audits
The reports reveal a critical gap in security practices among many projects. Out of 41 hacked projects analyzed, only seven had undergone the relevant audits. This alarming statistic underscores the vital importance of thorough security measures in preventing large-scale exploits, including regular audits and robust bug bounty programs.
History has shown that projects that prioritize these security measures are less likely to fall victim to attacks, signposting a clear path to better security.
Conclusion
As we move forward, a collaborative effort between developers, security researchers, and users will be crucial in building a more resilient and secure crypto ecosystem. The industry must prioritize security measures to protect users and maintain trust. By learning from these incidents, implementing stronger security protocols, and fostering a culture of vigilance, the crypto ecosystem can work towards a more secure future for all participants.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.

.png)
.png)


.png)