Introduction
Cardano, one of the top ten blockchains by market capitalization, is an established decentralized network with a growing ecosystem that aims to provide a more secure, reliable, and sustainable ecosystem for cryptocurrencies, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized applications (Dapps).
What sets it apart from other public blockchains is its scientific philosophy and meticulous, academic nature, which has seen it develop at a much slower pace than rivals like Solana and even Ethereum as the world’s first peer-reviewed blockchain. With so many new security threats draining user funds in the Web3 space, this tortoise vs hare approach and emphasis on longevity is not necessarily a bad thing.
Cardano was founded in 2015 by Charles Hoskinson, one of the co-creators of Ethereum.
Hoskinson famously left Ethereum in 2014 due to a dispute with one of Ethereum’s well-known faces, Vitalik Buterin, over the commercial route the network should take.
Cardano continues a course that connects all Web3 technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI). In 2020, IOHK (the developer of Cardano) and SingularityNET Foundation announced that a significant portion of SingularityNET’s decentralized protocol and platform had been ported from Ethereum to Cardano. The partnership is continuing to blossom, with big strides being made to soon enable AGIX staking on Cardano, according to the latest SingularityNET report.
What is Cardano?
Cardano is an open-source, decentralized public blockchain for building and deploying Dapps, digital assets and more to help serve a variety of purposes for the common good, especially in less developed countries.
Developed by Input Output HK (IOHK), Cardano is a research-driven, flexible layer-1 blockchain written in the Haskell programming language with a sustainable and scalable design. It takes a long view to the development of its network, prioritizing security over being first to market.
Launched officially in 2017, Cardano finally added its Plutus smart contract functionality in September 2021 with its successful Alonzo hard fork. This opened the blockchain platform to the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector while being interoperable through bridges with Ethereum, EVM chains and non-EVM blockchains.
Smart contract capabilities are needed to help build a robust, secure, scalable, and energy-efficient blockchain platform for building Dapps.
What is ADA?
Cardano got its name from Gerolamo Cardano, an Italian mathematician. Its native currency, ADA, is named after English mathematician Ada Lovelace.
ADA currently has a market cap of over $10 billion and a fully diluted value (including all potential tokens) of $13 billion. The ADA coin can be used to send and receive payments, cover transaction fees on the Cardano network, or for staking (through pool delegations), trading, or just simply a long-term HODL investment. It can be easily bought and sold on the open market or almost all leading crypto exchanges.
ADA Tokenomics
ADA has a maximum token supply of 45 billion, with an inflationary emission rate. There are currently already 35 billion ADA in circulation, and it has the following token distribution:
- 57.60% is allocated to ICO
- 11.50% is allocated to the Team
- 30.90% is allocated to Staking Rewards

Cardano Basics: How Does the Cardano Chain Work?
Architecture
Cardano uses a unique two-layer architecture system to meet its goals of sustainability and scalability. The two layers are:
- Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL), whose purpose is to account for value and handle transactions
- Cardano Computation Layer (CCL), whose primary purpose is the execution of smart contracts and Dapps. This splitting is required to allow Cardano to have a high throughput.
Cardano Programming language: Plutus (Haskell)
Cardano has a unique native smart contract language called Plutus to ensure that smart contracts are executed correctly. Plutus Core is a Turing-complete script written in the functional programming language Haskell, which makes it fully testable in isolation. Plutus Core forms the basis of the Plutus Platform – a development platform to develop Dapps on Cardano.
Consensus mechanism: Ouroboros (PoS)
Cardano uses Ouroboros, a unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism that is provably secure and energy-efficient. This is different from the proof-of-work (PoW) used by Bitcoin. PoW, a consensus mechanism popularized by Bitcoin, relies on miners who use highly specialized equipment to be the first to solve a time-consuming math puzzle.
While it scores big on decentralization, it’s high on energy costs and low on speed.
PoS does not demand as much energy as PoW and provides a more sustainable solution. Instead of miners staking their energy costs, PoS relies on validators who stake their cryptocurrency to validate transactions.
The Cardano network is distributed across staking pools. Each stake pool has a slot leader who is rewarded for verifying and adding new blocks to the chain. ADA holders may stake their tokens to specific stake pools, thereby increasing their chances of being chosen as stake leaders and enjoying rewards.
Layer-2 scaling: Hydra
It’s well-documented that Cardano can be a bit slow, with a current max of around 6 transactions per second, and an average of only 2TPS.
In May 2023, the Hydra Head layer-2 scaling solution went live on Cardano’s mainnet to help speed up the network and boost its DeFi capabilities whilst lowering transaction fees. Speculation that it can handle up to 1 million TPS is probably unrealistic, but what is certain is that it will significantly speed up and scale Cardano transactions once it’s optimally operational.
Cardano Background
Let’s take a look at the teams and communities behind this fascinating chain.
Cardano was launched in 2017 as a third-generation blockchain (Bitcoin is a first-generation chain while Ethereum is a second-generation one) and started life as an ERC-20 token before it migrated to its own mainnet.
It is closely tied to three entities that provide the infrastructure, tools and services it needs to scale – the Cardano Foundation, Emurgo, and IOHK.
- The Cardano Foundation is a Swiss-based non-profit organization that oversees the worldwide development and advancement of Cardano in enterprise applications. Apart from supporting and engaging with the Cardano community, The Cardano Foundation helps to build the tools that the Cardano community requires to solve problems in new, innovative ways.
- Input Output Hong Kong (IOHK) is a blockchain infrastructure and engineering company founded by Hoskinson and Jeremy Wood in 2015 that is contracted to design, build, and maintain the Cardano platform.
- Emurgo is Cardano’s founding entity and provides services and products to builders that drive Cardano’s push into the Web3 ecosystem.
Cardano’s Use Cases and Ecosystem
ADA, Cardano’s native cryptocurrency, has seen a surge in adoption in the U.S., and this is fueling the growth of its ecosystem.
Cardano’s ecosystem – which will be covered in a follow-up article – spans Web3, DeFi, NFTs, gaming, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), the metaverse, and more. These are the key areas that continue to propel the crypto industry forward as a whole.
But how do you explore and learn more about Cardano and its ecosystem?
Here are three DYOR (do-your-own-research) tools at your disposal:
- CardanoCube
CardanoCube is a platform for discovering and exploring projects and Dapps building on Cardano. This is important for stakeholders such as investors and developers who need to have a clear picture of the ecosystem before taking a plunge.
The platform wants people to have up-to-date, accurate information about the Cardano ecosystem and the developments happening around it.
- CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko
In crypto, all research often starts with CoinMarketCap and/or CoinGecko, the world’s two most popular crypto data aggregation platforms. Both have dedicated landing pages solely for the Cardano ecosystem, namely:
CoinMarketCap Cardano ecosystem projects
CoinGecko Cardano ecosystem projects
- DeFiLlama
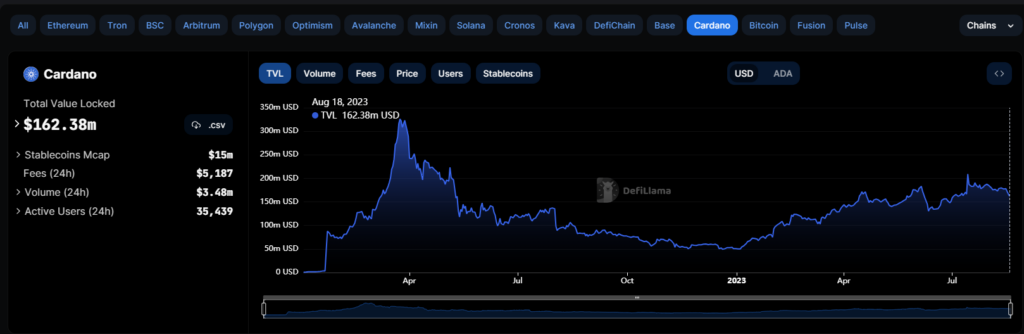
A vital tool in any DeFi degen’s arsenal is DeFiLlama. Use it to find out what’s happening on-chain on Cardano and its most popular Dapps like decentralized exchanges.
According to its Cardano page, the network currently has a total value locked (TVL) of $162 million and 35,400 active users.
What Can Cardano Be Used For?
Due to its versatility and scalability, Cardano has a myriad of use cases. The biggest at present are:
- DeFi
Much like Ethereum, the Cardano platform can be used to build and deploy DeFi protocols such as lending protocols. A core vision for Hoskinson and IOHK is to create a new financial system for emerging markets and to help “bank the unbanked” in less developed countries, that is people who do not have access to traditional financial services.
DeFi on Cardano therefore is a crucial component to the success of the chain’s vision, and makes the implementation of scaling solutions like Hydra and other new products even more important.
- Supply chain management
The platform can be used to implement secure and transparent supply chain solutions to ensure the traceability and authenticity of products. In 2021, Cardano rolled out an anti-counterfeiting supply chain solution.
- Voting and governance
The platform can be used to build tamper-proof voting solutions
- Identity verification
Cardano can be used to protect people’s identity by building decentralized identity verification systems, which will also help people without official government IDs gain access to decentralized financial services such as micro-loans and potentially universal basic income.
Cardano’s Push in Developing Nations
New technologies and innovations usually favor first-world countries. However, Cardano wants to take a different approach by starting with Africa.
How does Cardano see opportunities in Africa?
Cardano wants developing nations to break free from the traditional banking system (about 45% of people in Sub-Saharan Africa don’t have access to financial services), expensive middlemen, and political structures that favor a few. The blockchain platform sees an opportunity in Africa where the continent’s young population is more receptive to new technologies.
Third world countries stand to benefit a lot from blockchain technologies. This is because they rely on legacy systems of government that usually have big, open backdoors for corruption. It is estimated that developing nations lose $1.26 trillion annually to corruption, tax evasion, and theft. By using automated blockchains, African nations could close the tap of corruption.
This focus on emerging markets sets Cardano apart from almost all other blockchains and could set it on a course of explosive adoption for decades to come.
Final Thoughts on Cardano
Cardano distinguishes itself from its peers through a 2-layer architecture and a commitment to sustainability. Its use cases range from staking to leveraging the power of smart contracts. The Cardano platform offers developers, investors, and other crypto stakeholders several opportunities to engage with the ecosystem, which is growing in leaps and bounds since its launch.
Join us for our next article on Cardano which will take a closer look at its ecosystem and use cases.
Let us know your thoughts! Sign up for a Mindplex account now, join our Telegram, or follow us on Twitter.














.png)
.png)


.png)